Health: Understanding Gout Disease
Not all joint swelling is harmless. When should swelling be further examined, when does it become chronic, and how can it be treated? An outline of gout disease.

Gout is a condition of chronic joint inflammation accompanied by swelling and intense pain in various joints of the body, particularly in the big toe. It is a chronic disease caused by the deposition of uric acid crystals found in joint fluid, triggered by high acidity levels in the blood.
Symptoms
Swelling, severe pain, and redness at the center of the big toe, mostly affecting the foot, but also occurring in knees, ankles, or hands.
Who is affected?
While more common in older men, it can also affect women.
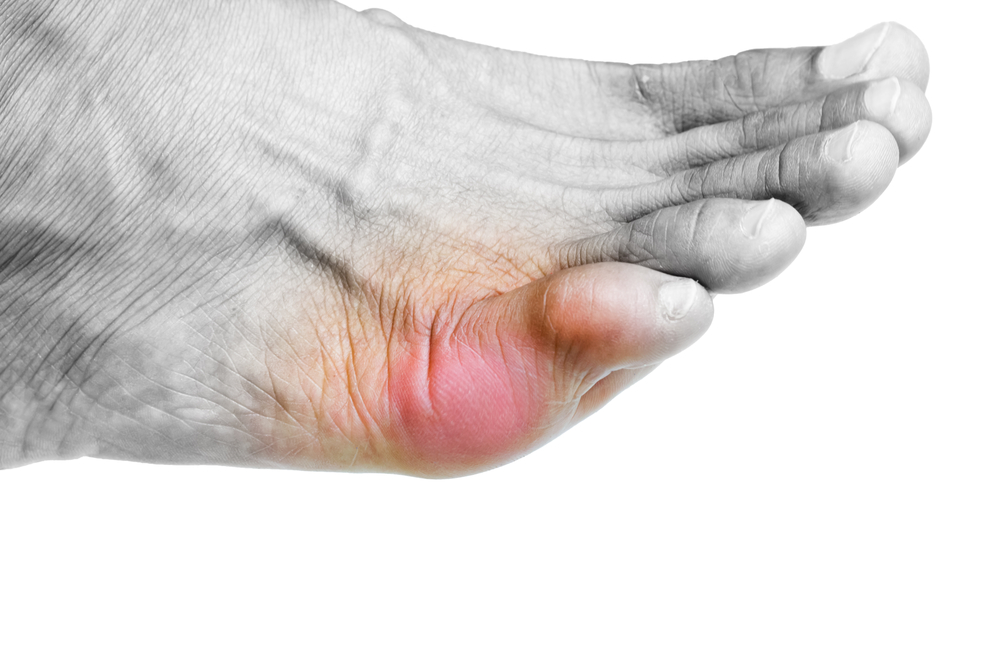 Gout Disease (Photo: Shutterstock)
Gout Disease (Photo: Shutterstock)How is it diagnosed?
In the laboratory: Material drawn from the inflammation site is sent for microscopic examination to look for uric acid crystals (appearing as needle-like structures). Additionally, the patient should request a blood test to measure uric acid levels.
Treatment
Involves two types of medications - one reduces uric acid production in the blood, and the other increases its excretion from the body.
Frequency
While some patients report a one-time occurrence of the disease, others experience recurrent gout attacks sporadically. Most attacks last a few days, but chronic gout may last longer.
When to seek medical treatment?
Whenever a severe pain accompanied by swelling is felt around the joints of the upper and lower limbs.
Which foods should those with gout consume less of?
Any food rich in uric acid - namely meat, sardines, mushrooms, and similar products.

