Understanding and Managing Heel Pain: Recognizing, Treating, and Coping with Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick tissue at the bottom of the foot, causing intense pain. Here you'll find comprehensive information about common causes, symptoms, and the most effective methods for treatment and daily management, including tips for rest, stretching, and advanced medical treatments.
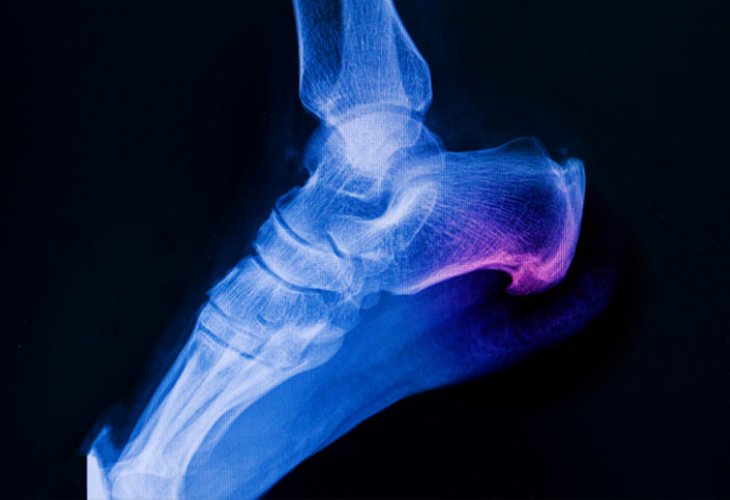 (Photo: shutterstock)
(Photo: shutterstock)The condition known as plantar fasciitis is one of the most common foot ailments. It involves inflammation of the thick tissue at the bottom of the foot, connecting the heel bone to the toes. This inflammation can cause severe pain and often disrupt daily activities.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis can present in various ways, accompanied by additional symptoms. Common symptoms include:
Foot Pain
Foot pain is the primary symptom of plantar fasciitis. Typically occurring in the heel area and spreading along the tissue, the pain can be sharp or dull, often worsening in the morning after getting out of bed or after prolonged rest.
Foot Stiffness
Those with plantar fasciitis may feel stiffness in the foot, especially after long periods of rest or in the morning. While it may ease over time with movement, it can return after standing or walking for long periods.
Swelling
In severe cases, swelling may occur in the heel area or along the tissue due to inflammation, potentially worsening without treatment.
Sensation of Pins and Needles
Some individuals experience a stabbing sensation in the foot, primarily in the heel area, particularly intense in the morning or after long periods of rest.
Difficulty Walking
In severe cases, the pain and stiffness can make walking difficult. Those with plantar fasciitis may alter their walking style to alleviate pain, potentially leading to additional musculoskeletal issues.
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
Several possible causes of plantar fasciitis include:
Excessive Foot Stress
Excessive stress on the foot is a common cause of plantar fasciitis. Activities such as running, prolonged walking, standing for extended periods, and working on hard surfaces can exert pressure on the tissue, leading to inflammation.
Foot Structure
Foot structure can be a significant factor in developing plantar fasciitis. Individuals with high or very flat arches are at higher risk due to improper pressure on the tissue, resulting in inflammation.
Excess Weight
Excess weight increases pressure on the foot and tissue, which may lead to inflammation. Overweight individuals are at heightened risk, especially if they stand or walk a lot.
Age
As people age, the foot tissues may lose elasticity, leading to increased vulnerability to inflammation. Individuals over 40 are at higher risk for developing plantar fasciitis.
Improper Exercise
Incorrect or overly strenuous exercise can cause excessive foot stress and tissue inflammation, highlighting the importance of controlled exercise and suitable footwear.
Inappropriate Footwear
Unsuitable shoes, particularly those lacking adequate support or with overly soft soles, can stress the foot and lead to plantar fasciitis.
Poor Posture
Standing or walking with poor posture can stress the tissue and cause plantar fasciitis. Improper postures include prolonged standing on one foot or distorted walking.
Treatment Methods for Plantar Fasciitis
Several treatment approaches for plantar fasciitis include:
Home Treatments
* Rest - Resting is a fundamental and critical treatment for plantar fasciitis. Reducing stress on the foot allows the tissue to heal and reduces inflammation. It is advised to avoid prolonged standing, extensive walking, and running during periods of sharp pain.
* Ice - Applying ice can help reduce inflammation and pain. It's recommended to apply ice to the heel area for 15-20 minutes a few times daily, especially after physical activity or prolonged standing.
* Stretching - Exercises that stretch the tissue and calf muscles can help ease pain and reduce stiffness. Simple stretches using a towel or stretching the foot muscles can be beneficial.
* Foot Support - Proper foot support can reduce pressure on the tissue and alleviate pain. Orthotic insoles, heel pads, or supportive shoes can be used.
Medical Treatments
* Medications - In cases of severe pain or inflammation, doctors may recommend painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications.
* Physical Therapy - Physical therapy is an effective treatment for plantar fasciitis and includes exercises to strengthen foot and calf muscles, stretching, and pain management techniques. A physical therapist may recommend supportive devices like elastic bandages or taping.
* Injections - In severe cases where home treatments and medications don't help, doctors may suggest steroid injections into the inflamed area to significantly reduce inflammation and pain.
Advanced Treatments
* Laser Therapy - Low-intensity laser therapy is an advanced technique for treating plantar fasciitis, improving blood flow, and accelerating tissue recovery, particularly effective in chronic cases.
* Shockwave Therapy - Shockwave therapy is another technique for treating plantar fasciitis, creating micro-traumas in the tissue to stimulate the body's natural healing process. This is notably effective in chronic cases where other treatments have failed.
* Surgery - In rare cases where all other treatments fail and pain persists, surgery may be recommended. This involves releasing the tissue from the heel to reduce pressure and pain, usually performed if pain and inflammation continue to disrupt daily life.
Daily Coping with Plantar Fasciitis
Creating a Supportive Environment
Using shoes with good support and proper foot support is essential for daily coping with plantar fasciitis. Shoes with sturdy soles and arch support can reduce tissue pressure and ease pain.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy body weight can help reduce foot and tissue pressure, easing pain and preventing future inflammations.
Adapted Physical Activity
Performing suitable and moderate physical activity can help keep the tissue flexible and prevent pain. Activities like swimming and Pilates can be particularly beneficial for those with plantar fasciitis.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Stretching and strengthening exercises for the foot and calf muscles can help reduce pain and improve flexibility. Simple exercises like towel stretches or stair edge stretches can be helpful.
Use of Orthotic Insoles
Using custom orthotic insoles can help reduce tissue pressure and alleviate pain. These insoles provide proper foot support and even pressure distribution.
Rest and a Healthy Lifestyle
Adequate rest and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce inflammation and enhance recovery. Ensuring sufficient sleep, proper nutrition, and moderate physical activity is important.
Consulting Experts
In cases where plantar fasciitis significantly impacts quality of life, consulting specialists for advice and appropriate treatment is crucial. Consulting with an orthopedist, physical therapist, or advanced treatment specialist can help find suitable solutions and manage the condition effectively.
In conclusion, plantar fasciitis is a common condition that can significantly affect quality of life. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and learning about various treatment options can help manage it better. Remember, each person experiences plantar fasciitis differently, so finding the right treatment is crucial. Through creating a supportive environment, weight management, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, it is possible to manage plantar fasciitis and reduce pain and inflammation.

