Psoriasis: Understanding and Managing a Chronic Skin Condition
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder marked by red patches and silvery scales. Discover the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments, with tips for daily management to enhance the quality of life for those affected.
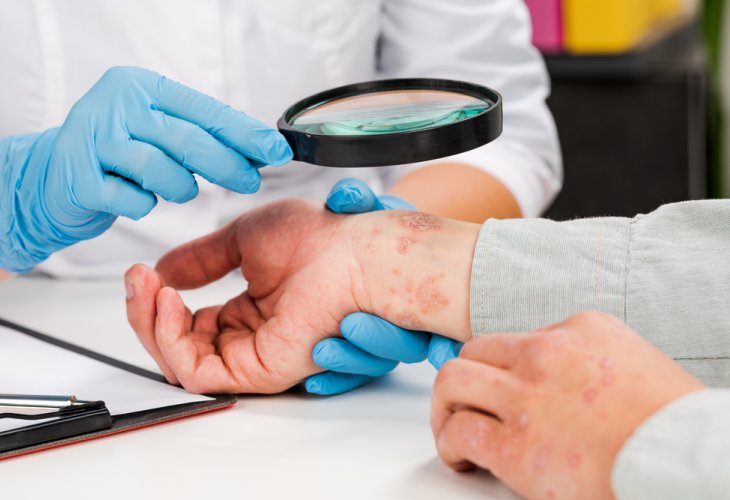 (Photo: shutterstock)
(Photo: shutterstock)Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition marked by red patches covered with silvery scales. The disease alternates between flare-ups and remission, impacting the quality of life for those who suffer from it.
Causes of Psoriasis
The precise cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is recognized as an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks healthy skin cells. Various contributing factors can lead to the onset or exacerbation of the disease.
Genetics
Genetics play a major role in psoriasis development. Research shows a higher risk for individuals with first-degree relatives suffering from psoriasis. Certain genes related to the immune system and inflammatory response are implicated, particularly those tied to autoimmune mechanisms. The combination of different genetic factors can influence the likelihood of developing the disease and the severity of symptoms.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can trigger or worsen the disease in genetically predisposed individuals. Significant environmental influences include:
* Infections: Viral and bacterial infections can prompt an immune response leading to psoriasis flare-ups. Especially, upper respiratory infections like strep throat are known triggers.
* Skin injuries: Injuries, cuts, burns, or abrasions may cause an inflammatory response that activates psoriasis, known as the "Koebner phenomenon".
* Weather: Cold, dry weather can exacerbate psoriasis, while warm, humid conditions may relieve symptoms. Dryness and skin irritation are risk factors for flare-ups.
* Stress: Chronic stress can intensify psoriasis and increase the frequency and severity of intractable flares through impacting the immune system and heightening inflammation.
Associated Conditions
Other medical conditions can elevate the risk of developing psoriasis and aggravate the disease:
* Psoriatic arthritis: An autoimmune disorder affecting joints causing pain and swelling. About one-third of people with psoriasis also have psoriatic arthritis.
* Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes patients have a heightened risk of psoriasis due to chronic inflammation and immune system changes.
* Obesity: Obesity is connected with chronic inflammation and metabolic alterations that increase psoriasis risk, worsen symptoms, and complicate treatment.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis symptoms vary in severity and location on the body. Common symptoms include:
Red Patches
Red patches are the hallmark of psoriasis, raised on the skin and covered with silvery scales. They can appear on various body parts, including:
* Elbows: One of the most common areas for psoriasis patches.
* Knees: Patches frequently appear on knees, causing discomfort when bending or stretching legs.
* Scalp: Psoriasis on the scalp can cause dandruff-like flaking, irritation, and redness, occasionally spreading to the forehead, nape, and ears.
* Lower back: Patches can also occur on the lower back, particularly in areas with consistent pressure or friction.
Itching and Pain
Psoriasis patches may come with itching and pain, creating significant discomfort. These symptoms can lead to additional effects:
* Cracking and bleeding: Ongoing itching can dry out the skin, leading to cracks and potential bleeding or infection.
* Severe nighttime itching: Intensified itching at night can impair sleep quality, affecting daily functioning and mental well-being.
Nail Symptoms
* Thickened nails: Nails may thicken, becoming more robust and durable.
* Color changes: Nails can change to a yellowish or brown hue.
* Nail detachment: In severe cases, nails may separate from the nail bed, a condition known as onycholysis.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a severe psoriasis symptom affecting joints. Characteristics include:
* Joint pain and swelling: Causes pain and swelling primarily in fingers and toes.
* Morning stiffness: People with psoriatic arthritis may experience morning stiffness that improves throughout the day.
* Movement limitations: Inflammation can restrict movement and daily function, complicating simple tasks.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Psoriasis treatment varies based on severity and symptom location. Main treatment goals are symptom relief and preventing flare-ups. Here are detailed treatment methods:
Topical Treatments
Topicals are initial, straightforward solutions for mild to moderate psoriasis. Common topical treatments include:
* Steroid creams and ointments: Potent anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce redness, swelling, and scaling. Medical supervision is required for prolonged use due to side-effect risks.
* Vitamin D and analogs: Creams containing vitamin D or its derivatives slow skin cell regeneration and reduce inflammation. These treatments are less harmful in long-term use than steroids.
* Topical retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that decrease inflammation and rapid skin cell growth. Caution is advised due to potential side effects like skin irritation.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy is a light treatment exposing skin to ultraviolet (UV) radiation under medical supervision. Two main phototherapy types include:
UVB Narrowband *: Utilizes special lamps emitting UVB rays at a specific wavelength. Treatment reduces rapid skin cell growth and alleviates inflammation.
PUVA *: Combines UVA light with a drug called psoralen, taken orally or applied topically, increasing skin sensitivity to UVA radiation. Used for severe psoriasis cases.
Systemic Medications
For severe psoriasis cases unresponsive to topical treatments and phototherapy, systemic medications are administered orally or by injection.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes can reduce attack frequency and severity:
* Stress management: Stress worsens psoriasis; therefore, practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or regular exercise is vital.
* Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol: Both can worsen psoriasis; abstaining is recommended.
* Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity worsens the disease and complicates treatment. Balanced eating and exercise help maintain a healthy weight.
* Proper diet: Eating more fruits, vegetables, omega-3-rich fish, and antioxidants can decrease inflammation and improve skin condition.
Daily Management of Psoriasis
Daily psoriasis management involves awareness and measures to alleviate symptoms and improve life quality. Important daily management aspects include:
Skin Care
Proper skincare is crucial for psoriasis management. Skin care tips include:
* Moisturizers: Regularly apply creams and oils to keep skin hydrated, preventing dryness and irritation.
* Avoid overly hot showers: Hot water can dry and irritate skin; use lukewarm water and limit shower time.
* Keep skin clean and hydrated: Avoid harsh, drying soaps; choose gentle, sensitive-skin-friendly products. Gently pat skin dry post-shower, avoiding vigorous rubbing.
Proper Diet
A suitable diet can positively affect skin health and reduce inflammation:
* Balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, omega-3-rich fish, and antioxidants helps decrease inflammation and affect skin health.
* Avoid inflammatory foods: Limit processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats that may exacerbate inflammation.
Stress Management
Psychological stress worsens psoriasis, making stress reduction strategies essential:
* Practice relaxation techniques: Tools like Pilates and breathing exercises aid relaxation and stress reduction.
* Regular physical activity: Moderate exercise can improve mood and lower stress levels.
Social Support
Social support is vital in coping with a chronic ailment like psoriasis:
* Support group participation: Joining psoriasis support groups offers support, information, and understanding.
* Family and friend support: Sharing the illness with loved ones and seeking emotional support can ease coping.
Medical Support
Proper medical resources utilization is integral in psoriasis management:
* Medication adherence: Follow prescriptions carefully and regularly consult with healthcare professionals.
* Ongoing medical advice: Continue consulting your healthcare provider for treatment adaptations and evaluation.
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease necessitating constant management. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments enhances life quality for sufferers. Topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic drugs, and lifestyle alterations help alleviate symptoms and manage the disease. A healthy routine and social support greatly aid daily psoriasis management.
Open: Efrat Barzel in a personal conversation about living with psoriasis

